Quantum Computing (QC) is here, it’s not quite mainstream yet but will be soon. When it does become mainstream, the cryptography approaches we use to secure our systems, our networks, and our data will be compromised. In 2019, DigiCert, the world’s leading provider of TLS/SSL and other digital certificates for websites, enterprise applications, and IoT, commissioned a survey by ReRez Research. They interview IT professionals from 400 enterprises in the US, Germany, and Japan. The findings of that research are published in the 2019 Post Quantum Crypto Survey report.
The survey found that many companies understand that there is a problem brewing and know that it will have to be addressed. But most don’t understand the significance of the risk, the urgency of starting to act now, or the importance of developing crypto-agility capabilities instead of just responding to issues when they happen. This lack of understanding is leading to a lack of preparedness and, ultimately, a higher likelihood that the company’s systems will be compromised.
The cryptography threat posed by quantum computing is real and big
Current cryptographic algorithms are mathematical algorithms designed to be difficult/impossible to break using classical computing. Unfortunately, they are relatively easy to crack using quantum computing. That is why post-quantum cryptography is so important. The industry needs to move to a new set of cryptographic algorithms based on harder mathematical problems that are difficult for both quantum and classical computers to process. While the quantum computers themselves aren’t here yet, the classic cryptographic algorithms are everywhere, and the world’s most sensitive data transactions use them.
When will this risk be realized, and how much time do companies have to prepare?
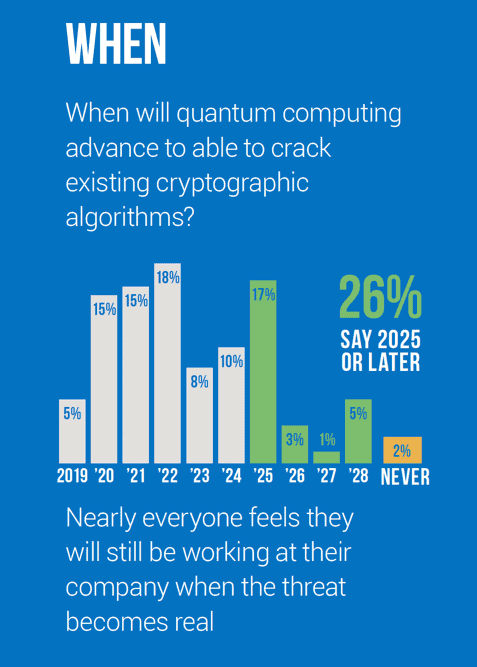 The risk may seem low, and the impact minimal if the arrival of quantum computing is still far off, but indications are that QC will arrive in the relatively near future. According to the PQC Survey, 74% of the IT professionals interviewed expect quantum computing to arrive and PQC capabilities to be needed within the next five years. Nearly 40% expect quantum computing to advance to be able to crack existing cryptographic algorithms by the end of 2021.
The risk may seem low, and the impact minimal if the arrival of quantum computing is still far off, but indications are that QC will arrive in the relatively near future. According to the PQC Survey, 74% of the IT professionals interviewed expect quantum computing to arrive and PQC capabilities to be needed within the next five years. Nearly 40% expect quantum computing to advance to be able to crack existing cryptographic algorithms by the end of 2021.
This means that companies only have 2-3 years to prepare, remediate, and upgrade their encryption systems before the quantum computing risk is realized. Certain products and systems in use today will be vulnerable when QC arrives. Certain security protocols used today will also become vulnerable. Meaning not only are future transactions at risk, but there is also a threat to today’s encrypted transactions. Stored transactions may be able to be decrypted in the future using quantum computing.
Companies are taking this risk seriously
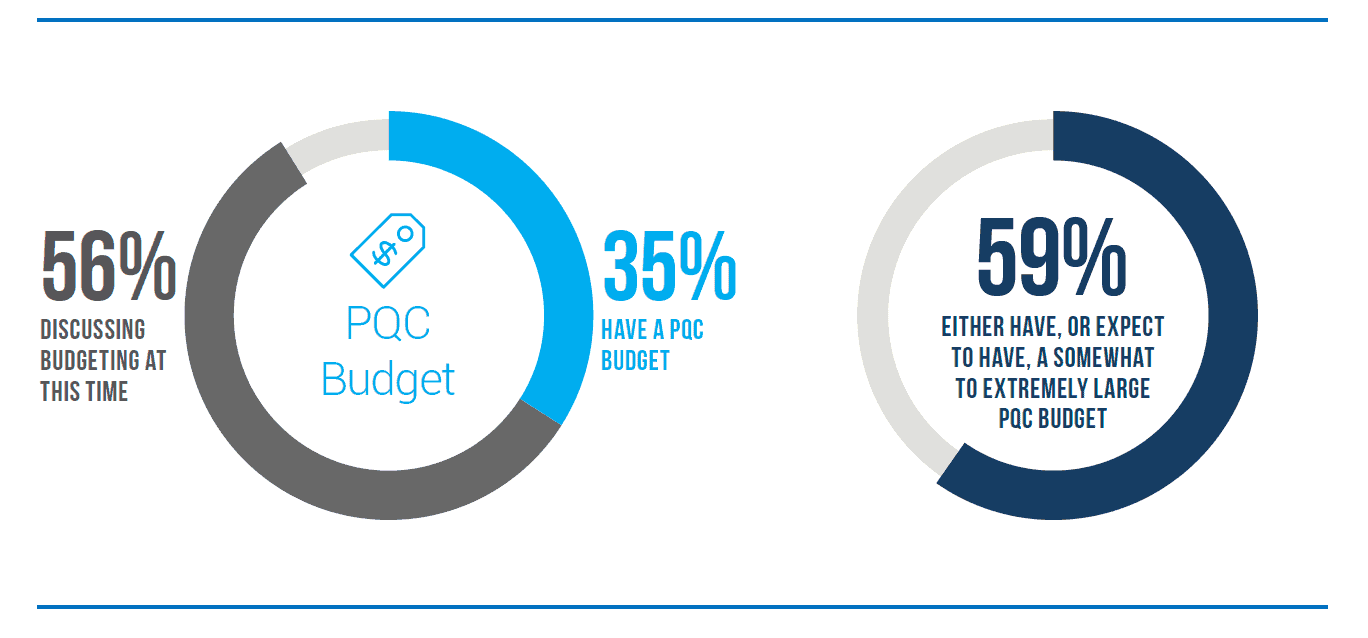
In the past, companies have been slow to respond to security risks like quantum computing – delaying action and investment until the risk is realized. The resulting remediation plans then took as much as 5-10 years to implement. The good news is that companies are taking quantum computing risks seriously. According to the PQC Survey, nearly a third of companies surveyed already have a QC budget and are actively working on remediation. Another 56% are working on establishing such a budget. Companies clearly understand there is both a challenge and a sense of urgency, and many have begun planning to do something.
 Mitigation strategies: Reacting vs. Preempting vs. Long-term agility
Mitigation strategies: Reacting vs. Preempting vs. Long-term agility
While many companies are planning to respond to the quantum computing threat, the Post Quantum Computing Survey found that the nature of mitigation strategies varied widely. Monitoring was (as expected) the most common tactic being used as companies seek to understand the risk and their exposure better. For companies seeking to preempt exposure through remediation, assessment of crypto-agility (the ability to upgrade encryption systems when vulnerabilities are discovered), and company risk (likelihood and impact) were common mitigation strategies. Rounding out the list of top mitigation strategies were knowledge building and development of best practices. Companies employing these tactics generally had already put monitoring and assessment capabilities in place.
Are your mitigation plans enough?
This is one of the most important questions companies should be asking. If you are just monitoring, will you be able to respond quickly enough to mitigate any impact? Do you understand your exposure, and are your remediation plans complete? Overlooking even one or two systems has the potential to leave your company vulnerable to attack. What happens if new threats emerge in the future? It’s great that the new Post Quantum Cryptography algorithms address the issues with the current encryption protocols, but what happens when the next breakthrough happens? Will your company be ready to respond? This is where crypto-agility is so important.
Decoupling crypto updates from deployment cycles
Businesses deploying IoT devices and systems with long life cycles may end up having products and systems still operating after the first quantum computers become a real cryptography threat. These once-safe products would then become a liability. An example would be automobiles with sensors, onboard computers, and connections to the internet. If quantum-safe strategies are not put in place today when manufacturing and deploying these devices, there is a reasonable likelihood of a breach in the future.
Crypto-agility is all about decoupling the lifecycle of the cryptography capabilities from the underlying products that depend on them. Products and deployed systems should be able to operate for a long time and deliver value to your company and customers. Cryptographic protocols need the ability to change and be updated on these products in response to new threats and mitigation strategies. Crypto-agility leads to business stability.
What should readers take away from this survey?
- Don’t wait! It is time to take the first few steps towards post-quantum cryptography now. These things take time, and if you want to complete the remediation and mitigation process before quantum computing arrives, time is of the essence.
- Develop agility — plan for the cryptography environment to start changing more quickly. Quantum computing is a revolutionary step forward in computational capabilities, but it won’t be the last. Just like your business needs to become more agile to respond to market opportunities, your systems need to become more agile to adapt to crypto threats.
![]()
The PQC survey was clear that companies understand that there are challenges and a sense of urgency around updating their cryptographic capabilities to prepare for quantum computing. Whether your company already has a PQC initiative underway or is still in the planning process. Now is a good time for you to start learning about the problem, and what solutions are available to help mitigate your risks. To be fully protected, businesses must begin to address the quantum computing threat today!
- Identify all the systems in your enterprise where cryptography is used.
- Assess what effort it will take to upgrade and remediate these systems.
- For 3rd party components or systems using 3rd party crypto capabilities, engage with vendors early to coordinate remediation plans.
- Add cryptography to your vendor evaluation process for future procurement. If vendors don’t have a plan around PQC, maybe they aren’t taking this threat seriously?
- Assess your company’s crypto-agility capabilities and risk exposure. Do you understand where you are vulnerable and your ability to respond in the event of a new threat?
- Develop best practices to improve your crypto awareness and maturity.
DigiCert is the industry leader in cryptography solutions for enterprises. DigiCert is doing the forward-thinking to anticipate what is comping and preparing you on how to prepare. A summary of the Post Quantum Cryptography Survey is available here. To help you apply these findings to your business, DigiCert recently released a PQC toolkit to help evaluate different technologies so you can better understand how they play within your infrastructure.
Related Articles
Quantum Computing – When Problems are too Complex for Classical Solutions
The State of Post-Quantum Cryptography – A New Report from the Cloud Security Alliance
Quantum Computing Problems
Quantum Computing (QC) is here, it’s not quite mainstream yet but will be soon. In 2019, DigiCert, the world’s leading provider of TLS/SSL and other digital certificates for websites, enterprise applications, and IoT, commissioned a survey by ReRez Research. They interview IT professionals from 400 enterprises in the US, Germany, and Japan. The findings of that research are published in the 2019 Post Quantum Crypto Survey report. The survey found that many companies understand that there is a problem brewing and know that it will have to be addressed. But most don’t understand the significance of the risk, the urgency of starting to act now, or the importance of developing crypto-agility capabilities instead of just responding to issues when they happen. This lack of understanding is leading to a lack of preparedness and, ultimately, a higher likelihood that the company’s systems will be compromised. The cryptography threat posed by quantum computing is real and big. Current cryptographic algorithms are mathematical algorithms designed to be difficult/impossible to break using classical computing. Unfortunately, they are relatively easy to crack using quantum computing. Companies only have 2-3 years to prepare, remediate, and upgrade their encryption systems before the quantum computing risk is realized.

