ICT stands for Information and Communication Technology which is a blanket term encompassing all the technologies and services involved in computing, data management, telecommunications provision, and the internet. These technologies all deal with the transmission and reception of information of some kind.
ICT permeates all aspects of life, providing newer, better, and quicker ways for people to interact, network, seek help, gain access to information, and learn.
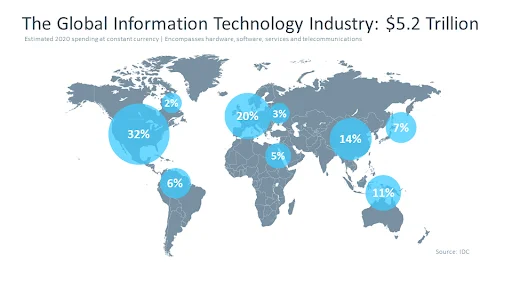
Besides its omnipresence, Information Communication Technology (ICT) has immense economic significance.
The United States is the largest technology market in the world, currently the industry is worth over US$440.20.The technology sector accounts for a significant portion of economic activity around the globe, as economies, employment, and personal lives become more digital, more connected, and more automated.
CompTIA’s Cyberstates report reveals that the economic impact of the technology sector in the US, measured as a percentage of gross domestic product, exceeds that of most other industries, including essential sectors such as retail, construction, and transportation.
But financial value is just one measure of the importance of Information and Communication Technology. ICT has great significance in many areas, as we’ll be exploring in this article.
Let’s dive in.
What is ICT?: Components of Information and Communication Technology
As the name implies, Information and Communication Technology (ICT) is a mixture of Information Technology and Communication Technology. Meaning, it comprises both hardware and software elements of Information Technology along with Communication Technology elements such as the Telegraph, Telephone and Television.
There are various elements in ICT such as,
Hardware: Which involves physical devices used to perform ICT operations, such as Computers, Servers, and mobile phones.
Software: Includes system software elements such as operating systems, and applications like MS Word, Excel and more.
Networks: Connectivity is the key component of ICT, this includes Internet, Local Area Networks, and Wide Area Networks.
Media/Visual Elements: ICT propagates the distribution of text, images, videos and any other medium through applications such as streaming platforms, and multimedia applications.
Data Management: Databases, Cloud management, and Data storage in general make up a big part of Information and Communication Technology.
Benefits of ICT: How Information and Communication Technology has improved Ties
Communication is a key component of the ICT mix. In recent years, Information and Communication Technology has evolved to make way for better connectivity among peers and industries.
Traditional on-premise private branch exchange (PBX) telephony systems built on hard-wired exchanges and equipment are giving way to a new telecommunications infrastructure, based on digital data transfer.
For instance, Voice over Internet Protocol (also known as Voice over IP, or VoIP) converts voice signals into a digital data stream that can be transmitted over network connections, offering long-distance and international communication at a fraction of the cost of standard telephone calls.
VoIP can be used on compatible telephone hardware, specialist VoIP handsets, desktop computers, and laptops, or via mobile apps.

Mobiles phones are undoubtedly one of the biggest byproducts of ICT. Smartphones have revolutionized the way information is consumed. With mobile phones, people now have a world of information, entertainment, and communications options, at their fingertips.
As per the new data released from GSMA Intelligence, there are currently over 5.4 Billion mobile phone users in the world, with over 120 Million users added just in the last 12 months.
A study by Reviews.org reveals that 66% of Americans check their phones 160 times every day. Almost the same number of people in the United States (65.7%) admit to sleeping with their smartphones at night.

It’s not difficult to understand the appeal. Besides voice and video calls, mobile users have instantaneous access to email, electronic fax (eFax), social media, and instant messaging (IM) tools. All of these are supported by a vast and growing ecosystem of mobile apps and online resources.
With the invention and leverage of Artificial Intelligence, these already prominent tools have become even more resilient. Applications that use AI are not only being embraced by organizations to double down their productivity but are also being used by individuals as a creative outlet.
Information communication technology (ICT) is now blurring the lines between telephony and the Internet. Organizations now have access to Unified Communications or UC, a platform based on VoIP that allows for the mixing of telecommunications with office productivity software, databases, multimedia, and online resources.
UC implementations can be localized within the enterprise, or made available to subscribers from the cloud, as an on-demand resource dubbed “Unified Communications as a Service” or UCaaS. This takes a cloud-based approach to integrating business communication tools into a single, streamlined platform.
These tools can include services like VoIP telephony, video conferencing, file sharing, collaboration, and instant messaging.
This approach highlights the consolidation and streamlining opportunities that ICT offers to the enterprise. Unified Communications as a Service can be an alternative to on-premises Unified Communications tools, a VoIP-only implementation, or a non-unified suite of business communication tools that include a mixture of cloud apps and traditional software from multiple vendors.

The Evolution of e-Commerce through Information and Communication Technology
There’s no doubt that the Internet, which is a vital part of ICT, has given rise to a new era of e-Commerce. What once powered a simple interface for transactions and record-keeping, has now dynamically changed the shopping experience. Today, consumers can shop for goods and services at the touch of their fingertips and from the comfort of their own homes
Cutting-edge tech like augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and artificial intelligence (AI) are enabling potential buyers to gain instant, interactive access to information on various products, and even to try them out in a range of simulated settings and environments.
ICT has helped commerce break all geographical barriers, bring consumers the luxury of convenience and help them make informed decisions about buying.
Besides the new avenues for purchasing and new methods of displaying and promoting commodities, eCommerce and the evolution of ICT have brought significant changes to how commercial organizations operate behind the scenes.
On the sales floor, mobile devices and real-time communications, coupled with advances in data analytics and artificial intelligence, enable retail assistants and sales personnel to adjust their pitches in line with the known purchase history and behavioural characteristics of individual customers.
Those same unified data management systems can also optimize the organization’s supply chain logistics, and facilitate customer fulfilment options like same-day delivery, or in-store pickup
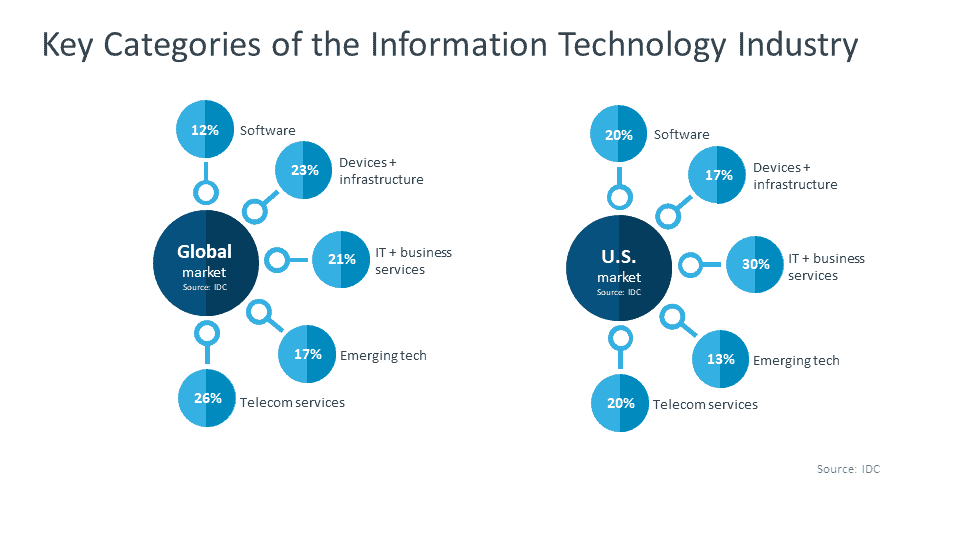
For organizations in the market for Information and Communication Technology solutions, developments in cloud infrastructure now present a rich vein of choices that include Software as a Service (SaaS) applications, data management tools, and various emerging technologies.
According to CompTIA.org, this market has a geographical variance in line with the level of technological maturity in different regions.
So, in the mature US market, for example, technology services and software account for nearly half of organizational spending. Countries with a lower level of development tend to allocate more spending to traditional hardware and telecommunications services.
In some developing economies where legacy infrastructure doesn’t exist, technology buyers find an easier path by jumping directly to the latest products and services.
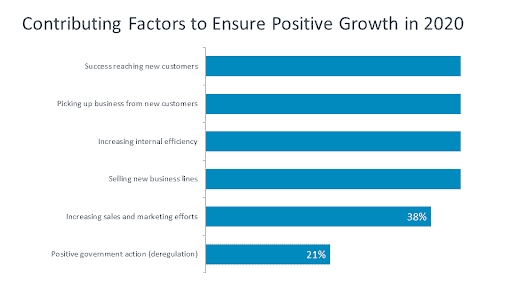
Managed services providers (MSPs) will need to concentrate on picking up additional business from existing clients by offering additional types or levels of services to grow their revenue and profit margins.
Organizations on both sides of the Information and Communication Technology supply chain will face the continuing challenge of sourcing ICT talent – either through recruitment of external candidates, or the training and “upskilling” of existing staff.
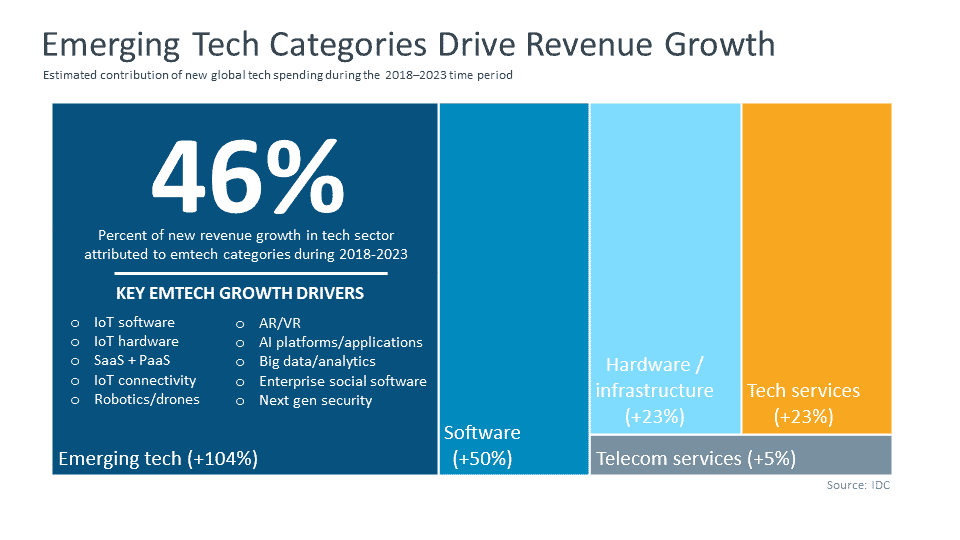
New Methods of Manufacturing in Information and Communication Technology
ICT is a useful support mechanism in the manufacturing sector, capable of rendering design and production that is more robust, effective, and efficient through the use of computer-based precision engineering, virtualized systems, and computer simulation.
Though concerns linger over the potential impact of trade volatility, tariffs, and the global economic slowdown, industry analysts have revealed that manufacturers have used new Information and Communication technologies to optimize their operations, maximize quality, and reduce costs.
Information and Communication Technology powers both customer feedback loops and data analytics empowering manufacturers to deepen their relationships with consumers, and add value to the products they create through customization.

Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have largely multiplied in recent years and helped manufacturers to optimize the speed, scale, and convenience of their operations.
They also facilitate the harnessing of performance data, which can be used to create smarter systems and models for all aspects of industrial operations, including supply chain management.
New communications technologies like 5G have started to minimize network latency, improve bandwidth, and increase the manufacturer’s capacity for real and near-real-time response.
5G integration with the Internet of Things or IoT technology has enabled manufacturers to increase their use of sensors, cloud platforms, centralized tracking, quality inspection, and other related systems.
Analysis of key performance metrics using sensor input, AI, and machine learning is enabling manufacturing organizations to harness the power of predictive analytics for performance enhancement and preventative maintenance. Using these technologies, adjustments can be pre-emptively made to improve efficiency and prevent untimely equipment breakdowns, saving time, resources, and money.
Physical robots and robotic process automation (RPA) are at the heart of Industry 4.0 and IoT operations. Physical robots can either function alongside human workers or take on tasks that might put human personnel at risk. Coupled with AI, robots, and automated processes can learn and evolve through on-the-job experience.
Additive manufacturing or 3D printing (AM/3DP) technology allows engineers to design innovative products that couldn’t otherwise be made using traditional manufacturing techniques. These technologies enable rapid prototyping and the construction of tools or parts in-house.
As 3D printers become more widespread and affordable, they also hold the potential to enable individuals to become localized manufacturers.

Information and Communication Technology is creating a new breed of “industrial wearables.” Tools and equipment such as smart glasses and biometric sensors can link individual workers with remote databases or industrial resources, and robotic exoskeletons that can multiply the strength of the wearer.
Overall, ICT is certainly an ally to manufacturing, embracing which will minimize the time and effort of production, streamline operations and improve the overall product quality.
Information communication technology (ICT) In Health Care
ICT has numerous applications in the healthcare sector – many of which have had a game-changing effect on patient care, public health, running costs, and the traditional bureaucracy associated with the medical profession and life sciences.
Electronic health records (EHRs) enable workers at healthcare institutions to input patient data into a central, digitized system that’s accessible to relevant stakeholders such as medical personnel, pharmacies, and insurers.
Systems can be integrated with user authentication and security policies to allow patient access to their health information, and configured with alerts and notifications in response to changing conditions. Cloud storage protects against the loss of sensitive data via strong backup and data recovery services.

Big data analytics may be applied at the therapeutic level in predicting epidemics, avoiding preventable deaths, developing new drugs or treatments, and improving efficiency and the general level of care.
Mobile devices and video transmission are central to “telemedicine” and “telehealth” provision, enabling practitioners to conduct two-way video consultations with patients or experts, and even to perform surgery while on a video call.
In a related manner, telemonitoring technology allows healthcare professionals to monitor vital signs, symptoms, and even patient blood levels from a remote location.
ICT holds tremendous potential for advancement and growth in the healthcare sector.
Empowering Education Through Information and Communication Technology
The education landscape has benefitted largely due to ICT. By melding database technology with communications and interactive programming techniques, ICT facilitates electronic learning or eLearning. Here, students from all walks of life can enjoy a self-paced education in subject areas limited only by the imaginations of the course creators.
eLearning platforms like Coursera and Lectora, for example, enable individuals and organizations to partake in vocational or special interest training courses combining formal instruction, quizzes, practical exercises, research, and interactive multimedia elements, all conducted in the learner’s own time, and at their own pace.

With literally a world of information to choose from, courses can pull in expertise and input from the highest levels of education and industry. And with access to the internet now available in some form to individuals across the globe, concepts like the Massive Open Online Course or MOOC are bringing educational opportunities to candidates who might otherwise miss out.
Many of the courses on offer originate from some of the most prestigious institutions of learning on the planet.
For schools and colleges, Information and Communication Technology provides students with an engaging, interactive, and self-paced model of learning which fosters their independence and involvement in the learning process, while also increasing their levels of digital sophistication and computer literacy.
ICT-powered learning projects enable teachers and instructors to contribute their own input while continuously analyzing and monitoring the progress of their students.
School management systems based on ICT allow administrators to use software and digital tools in automating various tasks, including research, library management, and general documentation.
Information and Communication Technology reduces the need for paper documents and the waste and bureaucracy that they traditionally create.
Information communication technology (ICT): Changing Our Impact on the Environment
Individuals, organizations and the government are on a quest to solve global challenges concerning the environment and increase sustainability using Information and Communication Technology.
Though, this presents something of a two-sided argument. Currently, ICT contributes up to 2.5% of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Contrastingly, however, many ICT technologies also help reduce these transmissions.
Besides the physical aspects such as a reduced reliance on paper-based documentation, ICT helps in monitoring climate change, mitigating and adapting to its effects, and easing the transition towards a green and circular economy.

The potential of Information and Communication Technology to solve climate-related issues is leading policymakers to seek commercial partnerships and initiatives with leading players in the industry.
In Europe for instance, the EU’s Directorate-General for Communications Networks, Content and Technology (DG CONNECT), is making environmentally conscious ICT a top priority as the organization pursues a climate-focused agenda.
Similarly, the ITU has established a new Focus Group on Environmental Efficiency for Artificial Intelligence and Other Emerging Technologies (FG-AI4EE), which will meet throughout 2020 to raise awareness about the environmental impacts of frontier technologies on a global platform.
The Group will investigate the ability of AI and emerging technologies to contribute to the achievement of the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals.
In conclusion, while ICT inevitably contributes to gas emissions, it also has an incredible potential to facilitate the reduction of those transmissions and offer promising solutions to global challenges.
Final Thoughts
Information and Communication Technology yields tremendous benefits for individuals, institutions, and society at large. By embracing the possibilities of the ICT sector, organizations and individual consumers can effectively transform Commerce, Education, Healthcare, and Lifestyle.
ICT breaks down barriers, whether it’s geographical or technical and enables communication, collaboration and connectivity on a global level.
Information and Communication Technology has a vast potential for change, but it comes with responsibility. Questions surrounding safety, data privacy, sustainability, and trust can only be resolved by combining technical expertise with social and environmental awareness.
All stakeholders in ICT must, therefore, be prepared to assume responsibility for all the changes that innovation can bring.
Summary:
- Information and Communication Technology (ICT) is a blanket term encompassing all the technologies and services involved in computing, data management, telecommunications provision, and the Internet.
- These technologies all deal with the transmission and reception of information of some kind. ICT permeates all aspects of life, providing newer, better, and quicker ways for people to interact, network, seek help, gain access to information, and learn..
- Communication is a key component of the ICT mix. In recent years, the merging of various kinds of technology has been increasing the number of options that people and institutions have for making contacts and keeping in touch.
- In retail and other customer-facing environments, the Information and Communication Technology infrastructure that once powered simple credit or debit card transactions and centralized record-keeping for commercial organizations continues to evolve, and eCommerce now integrates with the shopping experience itself.
- In the manufacturing sector, ICT is a useful support mechanism, capable of rendering design and production more robust, effective, and efficient through the use of computer-based precision engineering, virtualized systems, and computer simulation.
- As with manufacturing, ICT has numerous applications in the health care sector – many of which have had a game-changing effect on patient care, public health, running costs, and the traditional bureaucracy associated with the medical profession and life sciences.
FAQ
A: Information and Communication Technology (ICT) refers to the technologies used to manage and communicate information. It encompasses various digital tools, networks, and systems that enable the storage, retrieval, processing, and transmission of data. ICT is crucial because it facilitates efficient communication, enhances productivity, streamlines business operations, and enables innovation and collaboration in various sectors.
A: The benefits of ICT are manifold. Some of them are:
1. It enables rapid and seamless communication, both within organizations and across geographical boundaries, fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing.
2. ICT automates tasks, improves efficiency, and reduces manual errors.
3. It enables access to vast amounts of information, promotes research and learning, and empowers individuals and businesses with real-time data for informed decision-making.
4. Additionally, ICT drives digital transformation, creates new job opportunities, and contributes to economic growth.
A: 1. ICT has revolutionized education and learning by providing access to a wealth of educational resources, online courses, and digital platforms for remote learning.
2. It enables interactive and personalized learning experiences, facilitates communication between students and teachers, and encourages collaborative projects.
3. ICT enhances administrative processes in educational institutions, such as record-keeping, scheduling, and assessment, making education more accessible, inclusive, and efficient.
A: ICT plays a pivotal role in modern businesses and industries.
1. It enables efficient communication and collaboration among employees, departments, and global teams, fostering innovation and agility.
2. ICT streamlines business operations through automation, data analytics, and cloud computing, optimizing processes and enhancing productivity.
3. It enables online marketing, e-commerce, and customer relationship management, expanding business reach and improving customer experiences.
4. ICT also facilitates supply chain management, inventory control, and real-time monitoring, enhancing operational efficiency and decision-making.
A: Adopting ICT can present certain challenges. These include the initial investment and ongoing costs associated with infrastructure, software, and training. There might be resistance to change and a learning curve for employees adapting to new technologies. Cybersecurity and data privacy concerns also arise with the increased use of ICT.
Additionally, ensuring equal access to ICT resources and bridging the digital divide can be challenging in certain regions or demographics.